
The Story of Corrosion Testing in Endless Rod: Advancing Product Performance through R&D
by Luis Benavides, M.SC, P.Eng.
At Lifting Solutions, our approach to product testing and development is grounded in rigorous Research & Development (R&D) initiatives that enhance our understanding of material performance in real-world conditions. One such initiative, the corrosion testing of our Endless Rod (ER), exemplifies our commitment to engineering excellence and reliability in artificial lift systems.
THE ORIGIN OF CORROSION TESTING FOR ENDLESS ROD
The structured corrosion testing program emerged from a fundamental industry challenge: ensuring the long-term durability of rods operating in highly corrosive environments. In the field, ER is exposed to CO₂, H₂S, and chlorides or others all of which can impact its service life.
Recognizing these challenges, our engineering teams developed dedicated testing equipment and an associated evaluation process to quantify corrosion resistance and support product development and application.
Our methodology integrates real-world conditions to assess performance more accurately. Based on the widely adopted NACE TM0177 standard, we adapted our approach to gain deeper insights into how our products interact with different environments. This involved refining key parameters such as exposure durations, fluid compositions, and mechanical stress conditions to ensure a more precise understanding of the corrosion behavior of our ER products.
SPECIALIZED TESTING SETUP
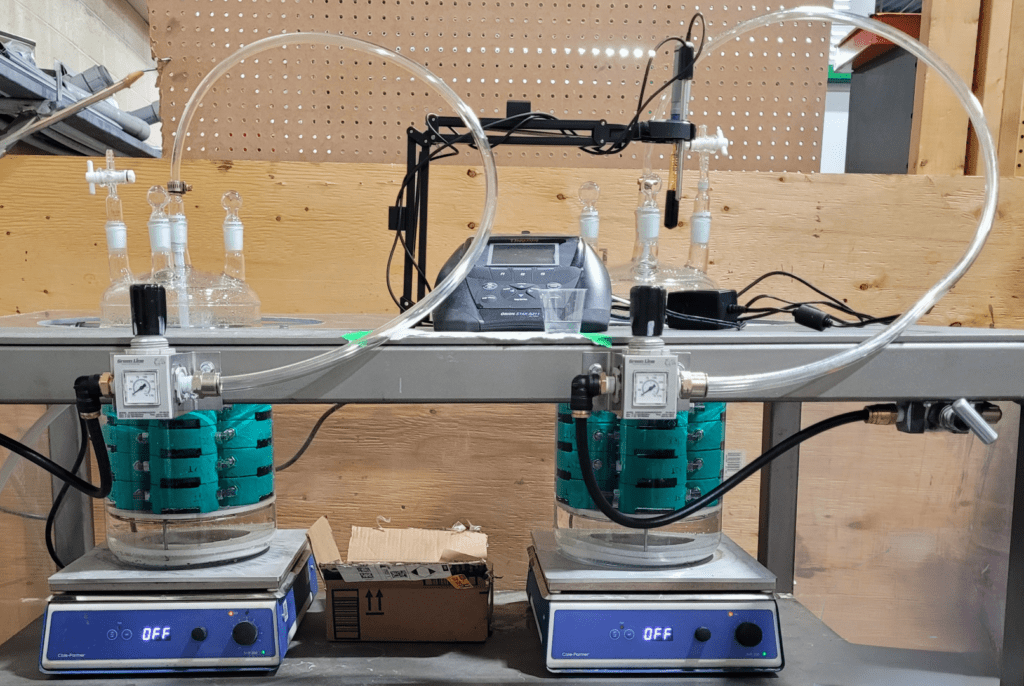

To conduct these evaluations, we utilize a dedicated corrosion testing system specifically designed for these studies. This setup consists of:
- A specialized corrosion testing bench equipped with pneumatic controls to regulate gas flow, pressure, and purge cycles within the system.
- Two borosilicate glass reactors, chemically inert and transparent, allowing for real-time observation of corrosion progression.
- A structured arrangement within each reactor, designed to securely hold samples in an organized manner, whether under applied stress or in a stress-free condition, ensuring controlled exposure to test conditions.
- Multiple inlet and outlet ports, enabling the integration of condensers and other equipment for various corrosion test configurations under different industry standards.
Each reactor houses test samples prepared in specific orientations, with defined exposed surfaces protected by corrosion-resistant coatings to ensure consistent evaluation of the areas of interest. The system supports two primary test configurations:
- Static corrosion exposure—assessing material behavior in a controlled environment.
- Stress-assisted corrosion testing—introducing tensile loads to evaluate the combined effects of mechanical stress and corrosion on rod integrity.
After stabilizing the test conditions—monitoring pH, temperature, and chemical concentration—the exposure period varies depending on the test standard being followed. Throughout the testing process, samples undergo dimensional, morphological, and weight-based evaluations to quantify corrosion rates in MPY and assess surface damage characteristics.
ADVANCING INNOVATION IN CORROSION RESEARCH
This initiative is part of our ongoing efforts to deepen our understanding of corrosion effects and optimize testing methodologies. By leveraging controlled evaluations aligned with industry standards, we aim to support continuous improvement in:
- Assessing Material Behavior: Gathering data on how different materials respond to corrosive environments under controlled conditions.
- Refining Testing Approaches: Ensuring structured and reliable methodologies that align with industry benchmarks.
- Supporting Product Application and Selection: Providing insights that help guide decisions in material and coating choices based on field conditions.
By integrating corrosion testing into our broader R&D framework, we reinforce our commitment to advancing knowledge in material science. As our research evolves, we remain focused on refining evaluation methods that contribute to better-informed product application strategies.